Blockchain for Beginners
What is Blockchain
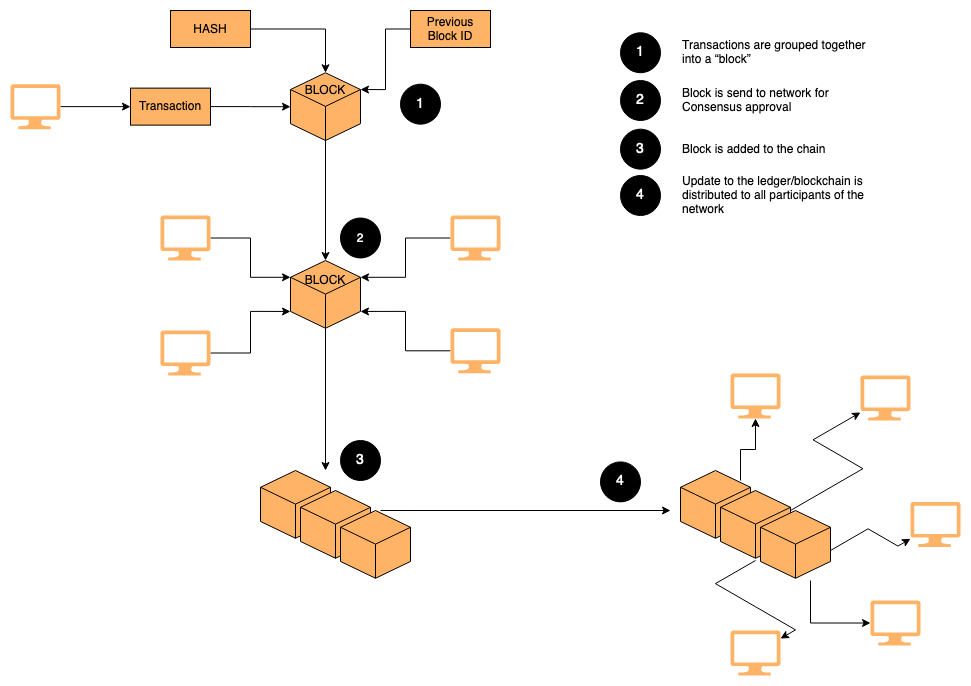
Blockchain technology is a technological implementation of a distributed ledger and was first developed as a solution for centralization. Blockchain can be described as a collection of records linked with each other into an immutable chain that preserves their chronological order and protected using Cryptography. Each member of the blockchain network maintains a copy of the ledger. Any update to the shared ledger requires approvals of the majority members of that network — using a pre determined consensus role and distributed to the system
Cryptocurrencies like BitCoin and Ethereum are some of the popular implementation of Blockchain technology. Blockchain technology was introdcuced by Satoshi Nakamato in 2008 with the implementation of Bitcoin.
eg: With Bitcoin network - financial transactions are grouped together into a “block” of transactions. These blocks are linked together and an identifical copy is stored on each of the computer systems(nodes) participating in the network. Hence the term "BlockChain". The first block on the blockchain is “block 0,” the next block after that is “block 1,” followed by “block 2” and so on. When a new block is added, it is connected to the previous block by referring to it within the block data. Block 1 includes a reference to block 0 as the previous block. These blocks of transactions act as a shared digital ledger of all the transactions that have occurred on the Bitcoin network
Some of the key elements of a Blockchain network are:
Nodes or computer network and their participation rules
Cryptography
Consensus rules for adding a new block
Different blockchain technologies have different rules for each of the key elements. Blockchain ledgers themselves are specific instances of ledgers that contain their respective transactions or records and there can be multiple instances of any blockchain technology. For technologists - this can be compared to the Relational Database (RDBMS) Ecosystem where there are multiple implmentation of RDBMS - MySql, PostgreSQL, Oracle Database, etc and each can hvave multiple different instances with their own seperate data and database.
Types of Blockchains
Public Blockchains: Bitcoin is an example of public Blockchain. Public blockchains is an implementation of a particular blockchain where anyone can join the network and all records on the ledger can be viewed and accessed by anyone without any approvals.
Private and Permissioned Blockchains: Enterprises have come up with use cases for a private and Permissioned blockchain even though Blockchain's was first invented by Satoshi for building a public and open trustless network without any central authority, .Private Blockchains are similar to public blockchains and share the same features of public blockchain such as shared nodes, immutable and shared ledger with the only difference being access to the network is Permissioned. Only pre-approved nodes can participate in this network.


